Peripateticism
Yuens' blog
YOLOv2 region层 Forward 部分 DarkNet 源码分析
- 代码仓库:pjreddie/darknet
- 代码版本:61c9d02ec461e30d55762ec7669d6a1d3c356fb2
- 代码日期:2018-09-14
本文以yolov2-tiny这个小网络为例进行分析,在此先给出网络执行流程图。
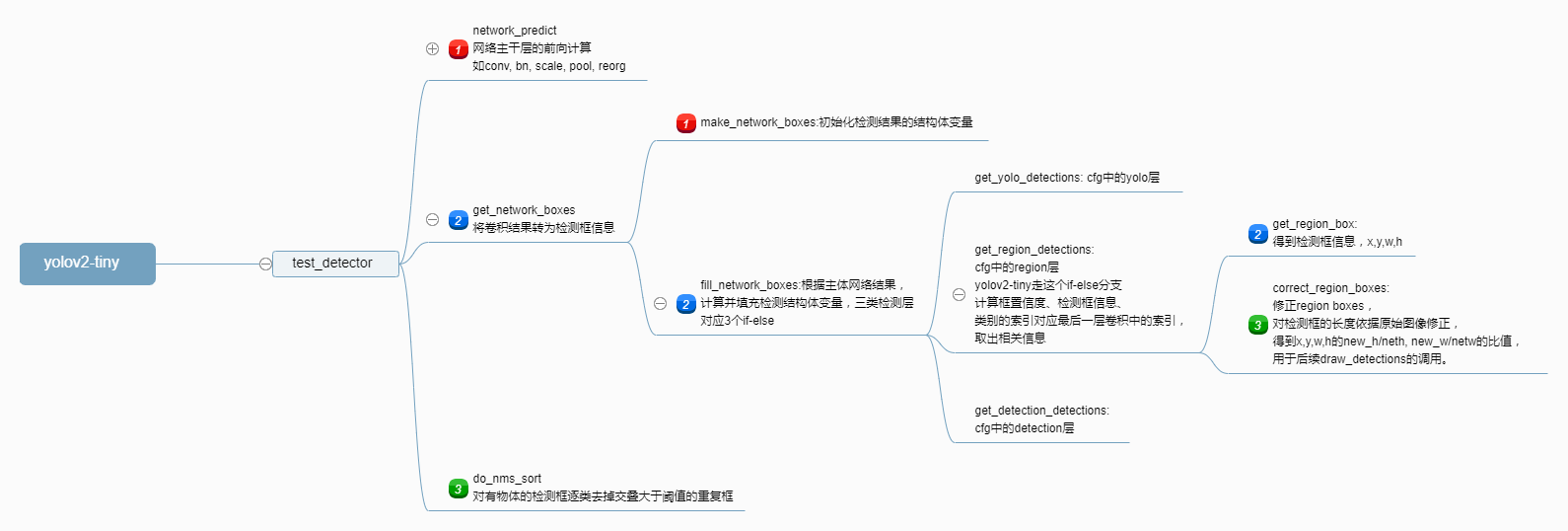
1. yolov2-tiny 网络结构与 Region 层参数
下面先给出其执行流程图和对应的region层在网络结构cfg文件中的定义,后面会对检测 region 层代码一步一步分析。
1.1 YOLOV2 网络结构
$ ./darknet detect cfg/yolov2-tiny.cfg yolov2-tiny.weights data/dog.jpg
layer filters size input output
0 conv 16 3 x 3 / 1 416 x 416 x 3 -> 416 x 416 x 16 0.150 BFLOPs
1 max 2 x 2 / 2 416 x 416 x 16 -> 208 x 208 x 16
2 conv 32 3 x 3 / 1 208 x 208 x 16 -> 208 x 208 x 32 0.399 BFLOPs
3 max 2 x 2 / 2 208 x 208 x 32 -> 104 x 104 x 32
4 conv 64 3 x 3 / 1 104 x 104 x 32 -> 104 x 104 x 64 0.399 BFLOPs
5 max 2 x 2 / 2 104 x 104 x 64 -> 52 x 52 x 64
6 conv 128 3 x 3 / 1 52 x 52 x 64 -> 52 x 52 x 128 0.399 BFLOPs
7 max 2 x 2 / 2 52 x 52 x 128 -> 26 x 26 x 128
8 conv 256 3 x 3 / 1 26 x 26 x 128 -> 26 x 26 x 256 0.399 BFLOPs
9 max 2 x 2 / 2 26 x 26 x 256 -> 13 x 13 x 256
10 conv 512 3 x 3 / 1 13 x 13 x 256 -> 13 x 13 x 512 0.399 BFLOPs
11 max 2 x 2 / 1 13 x 13 x 512 -> 13 x 13 x 512
12 conv 1024 3 x 3 / 1 13 x 13 x 512 -> 13 x 13 x1024 1.595 BFLOPs
13 conv 512 3 x 3 / 1 13 x 13 x1024 -> 13 x 13 x 512 1.595 BFLOPs
14 conv 425 1 x 1 / 1 13 x 13 x 512 -> 13 x 13 x 425 0.074 BFLOPs
15 detection
mask_scale: Using default '1.000000'
Loading weights from yolov2-tiny.weights...Done!
dog: 82%
car: 74%
bicycle: 59%
1.2 Region 层
这里列出最后一个卷积层和 Region 检测层,列出 Region 层的上一层(卷积)的原因是因为输出个数,与检测结果直接相关。
[convolutional]
size=1
stride=1
pad=1
filters=425
activation=linear
[region]
anchors = 0.57273, 0.677385, 1.87446, 2.06253, 3.33843, 5.47434, 7.88282, 3.52778, 9.77052, 9.16828 # anchors的值
bias_match=1
classes=80 # 类别个数
coords=4 # 坐标值: x,y,w,h
num=5 # anchors的个数
softmax=1
jitter=.2
rescore=0
object_scale=5 # loss中栅格中是目标的系数
noobject_scale=1 # loss中栅格中非目标的系数
class_scale=1 # loss中栅格中类别损失的系数
coord_scale=1 # loss中栅格中坐标损失的系数
absolute=1
thresh = .6
random=1
最后卷积层的输出维度为13 x 13 x 425 = 71825,输出元素个数与检测层一样,检测层的维度需要这么看:13 x 13 x 5 x (4 + 1 + 80):
- 对应将 resize 过后宽高为
416 x 416的原图,在经过 5 个stride = 2的max-pooling后为13 x 13,即将原图最后切分为13 x 13个区域; - 5 个 anchors ,对应每个区域有 5 种比例,那么会得到
13 x 13 x 5个检测框; - 4 个坐标参数(检测框的二维中心点坐标x、y、该检测框的高与宽h、w),1 个框的置信度 confidence 分数,以及 80 个概率值对应当前检测框 80 类物体中的存在概率。
所以,检测层对最后一个卷积的结果没有做变换,只是以训练预设的方式将最后一层卷积的结果解析出来。
2.锁定网络主干与检测起始位置
2.1 锁定网络主干
先看网络主干部分,按我们的理解,整个网络的计算应该会有循环来逐层计算,经过在代码里加入打印信息,可以定位在src/network.c中的forward_network函数,计算了每层的结果(找到这一层可以看命令的调用,所出发的代码,一步步加入打印信息,在这之前可以先看看darknet.h这一头文件,该头文件定义了darknet对层、网络的定义,看完后会对框架有一个大概的了解),也是在这里可以每一层的的结果打印出来。其forward_network函数内容如下:
void forward_network(network *netp)
{
#ifdef GPU
if(netp->gpu_index >= 0){
forward_network_gpu(netp);
return;
}
#endif
network net = *netp;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < net.n; ++i){
net.index = i;
layer l = net.layers[i];
if(l.delta){
fill_cpu(l.outputs * l.batch, 0, l.delta, 1);
}
l.forward(l, net);
net.input = l.output;
// print input here
if(l.truth) {
net.truth = l.output;
}
}
calc_network_cost(netp);
}
需要注意的是,打印的第i层的结果其实都是第i+1层的输入。因而打印最后卷积的结果,即检测的输入,即第15层的input,所以在上面代码打印处,需要判断i == 15。实际上面最后一层detection的计算并不在这个循环里,是一个后处理的过程。
取到最后一层卷积的结果,根据前面的网络执行结构图的输入输出信息,我们也可以最后一个卷积结果的元素个数是否是echo "13*13*425" | bc,从而确认是否执行到了最后一个卷积层。下一步就是看看检测这一后处理的计算过程。
2.2 锁定检测起始位置
仍旧在src/network.c中查找调用了forward_network的函数,发现是network_predict,仍旧是在该文件,发现调用network_predict的函数有多个:network_predict_image,network_predict_data_multi,network_predict_data,感觉这样找反而越来越多,那么反着麻烦,看正向的代码执行过程。
由于调用的命令是./darknet detect cfg/yolov2-tiny.cfg yolov2-tiny.weights data/dog.jpg,那么看看example/darknet.c中main函数的detect这部分代码(别急,再看一眼if-else结束,发现是return 0,那就可以放心了):
else if (0 == strcmp(argv[1], "detect")){
float thresh = find_float_arg(argc, argv, "-thresh", .5);
char *filename = (argc > 4) ? argv[4]: 0;
char *outfile = find_char_arg(argc, argv, "-out", 0);
int fullscreen = find_arg(argc, argv, "-fullscreen");
test_detector("cfg/coco.data", argv[2], argv[3], filename, thresh, .5, outfile, fullscreen);
}
深入test_detector探究,找到该函数位于examples/detector.c:562,这个函数很长,不过条理还算清晰,可以看到里面有调用forward_network的network_predict函数:
void test_detector(char *datacfg, char *cfgfile, char *weightfile, char *filename, float thresh, float hier_thresh, char *outfile, int fullscreen)
{
list *options = read_data_cfg(datacfg);
char *name_list = option_find_str(options, "names", "data/names.list");
char **names = get_labels(name_list);
image **alphabet = load_alphabet();
network *net = load_network(cfgfile, weightfile, 0);
set_batch_network(net, 1);
srand(2222222);
double time;
char buff[256];
char *input = buff;
float nms=.45;
while(1){
if(filename){
strncpy(input, filename, 256);
} else {
printf("Enter Image Path: ");
fflush(stdout);
input = fgets(input, 256, stdin);
if(!input) return;
strtok(input, "\n");
}
image im = load_image_color(input,0,0);
image sized = letterbox_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized = resize_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized2 = resize_max(im, net->w);
//image sized = crop_image(sized2, -((net->w - sized2.w)/2), -((net->h - sized2.h)/2), net->w, net->h);
//resize_network(net, sized.w, sized.h);
layer l = net->layers[net->n-1];
float *X = sized.data;
time=what_time_is_it_now();
network_predict(net, X); // 该函数调用了forward_network
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", input, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
//printf("%d\n", nboxes);
//if (nms) do_nms_obj(boxes, probs, l.w*l.h*l.n, l.classes, nms);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms);
draw_detections(im, dets, nboxes, thresh, names, alphabet, l.classes);
free_detections(dets, nboxes);
if(outfile){
save_image(im, outfile);
}
else{
save_image(im, "predictions");
#ifdef OPENCV
make_window("predictions", 512, 512, 0);
show_image(im, "predictions", 0);
#endif
}
free_image(im);
free_image(sized);
if (filename) break;
}
}
该函数显示了整个网络执行的轮廓,其中部分行代码被作者注释掉了,其实刚刚我们将代码跟到了network_predict函数,可以在上面这个函数里找到network_predict,其实现是将network_forward的结果直接返回,从这里我们开始,忽略掉网络初始化和后面处理的无关代码,简化后,我们只需要test_detector函数中以下代码的实现:
network_predict(net, X);
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", input, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms); // nms:.45,nms值前面写死的0.45,非0会执行do_nms_sort
draw_detections(im, dets, nboxes, thresh, names, alphabet, l.classes);
- 看了这部分代码,可以看出darknet给出的网络预测时间,实际上是不算后处理(nms,detect等)的网络执行时间;
- 从这个轮廓来看,检测层,也就是后处理部分大致有:
get_network_boxes、do_nms_sort两部分; - 执行结束
network_predict时,net这个结构体变量已经挂载了最后卷积的结果(具体说来是network_forward函数中有一句net.input = l.output;)。
到此,我们找到了检测层计算的起始位置。
3.检测层分析
刚已经说到检测层致有:get_network_boxes、do_nms_sort两部分。
3.1 检测层:获取检测框
接下来,上面代码中net被传给get_network_boxes得到det结构体,需要仔细看看get_network_boxes是怎么做的。这其中会有基于最后一层卷积结果的region层计算。其要点如下:
get_network_boxes流程如下:
make_network_boxes:初始化申请检测框结构体内存(检测框的定义可在include/darknet.h中找到detection与box结构体);fill_network_boxes:将检测层上一层(卷积)的结果填充到detection与box结构体变量中;get_yolo_detections:cfg中的yolo层,yolov2-tiny没有执行该层;get_region_detections:cfg中的region层,yolov2-tiny有该层;region层主体部分的计算;get_region_box;correct_region_boxes;
get_detection_detections:cfg中的detection层,yolov2-tiny没有执行该层。
经过以上两个大的步骤,得到了最后检测框的结果。
3.1.1 检测层:get_network_boxes
get_network_boxes位于src/network.c:589,函数实现如下:
detection *get_network_boxes(network *net, int w, int h, float thresh, float hier, int *map, int relative, int *num)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== get_network_boxes ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "int nboxes = 0;\n");
fprintf(stderr, "get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes)\n");
fprintf(stderr, "w:%d h:%d\n", w, h); // w:768 h:576 原始图像的大小
fprintf(stderr, "thresh:%f\n", thresh); // 0.500000 位于example/darknet.c:432-437,if-else在detect部分定义,若用户未定义则该值默认为0.5
fprintf(stderr, "hier:%f\n", hier); // 0.500000 位于example/darknet.c:432-437,if-else在detect部分定义,值为0.5
fprintf(stderr, "relative:%d\n", relative); // 1 位于example/detector.c:600,值被固定为1
detection *dets = make_network_boxes(net, thresh, num);
fill_network_boxes(net, w, h, thresh, hier, map, relative, dets);
return dets;
}
// 又看了下include/darknet.h中关于detection与box这两个结构体的定义
typedef struct detection{
box bbox;
int classes;
float *prob;
float *mask;
float objectness;
int sort_class;
} detection;
typedef struct{
float x, y, w, h;
} box;
该函数做了两件事:先调用make_network_boxes对detection结构体变量初始化,后调用fill_network_boxes填充值到其中。make_network_boxes先看看其初始化过程:
detection *make_network_boxes(network *net, float thresh, int *num) {
fprintf(stderr, "==== make_network_boxes ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "net->n:%d\n", net->n); // net->n:16
layer l = net->layers[net->n - 1]; // 拿到最后一层
int i; // 初始化 i 用来后面遍历 nboxes
int nboxes = num_detections(net, thresh); // 调用num_detection(net, thresh)获取到boxes的数量
fprintf(stderr, "nboxes:%d\n", nboxes); // nboxes:845
fprintf(stderr, "l.coords:%d\n", l.coords); // l.coords:4
if(num) *num = nboxes; // 初始时num作为指针传入,实际结果需要返回去
detection *dets = calloc(nboxes, sizeof(detection)); // 申请空间,nboxes个detection元素的结构体数组
for(i = 0; i < nboxes; ++i){ // 初始化每个detection box
dets[i].prob = calloc(l.classes, sizeof(float)); // 每个detection box都有一个classes元素个数的float *prob数组,对应当前box每个类别的概率
if(l.coords > 4){ // 坐标数目大于4放到mask中,coords定义在cfg文件中,即每个box的四个坐标,yolov1到v3的cfg文件中定义均为4
dets[i].mask = calloc(l.coords-4, sizeof(float));
}
}
return dets;
}
num_detections函数返回网络结果的box数量,其函数定义在src/network.c:538:
int num_detections(network *net, float thresh)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== num_detections ====\n");
int i;
int s = 0; // 返回box的数量
for(i = 0; i < net->n; ++i)
{ //该过程,累加YOLO、DETECTION、REGION类型的层的box
layer l = net->layers[i];
if(l.type == YOLO){
fprintf(stderr, "layer idx: %d type: YOLO\n", i);
s += yolo_num_detections(l, thresh);
}
if(l.type == DETECTION || l.type == REGION){ // yolov2和yolov2-tiny的网络配置cfg文件中,检测层定义均为region
fprintf(stderr, "layer idx: %d type: DETECTION || REGION\n", i); // layer idx: 15 type: DETECTION || REGION
fprintf(stderr, "l.w:%d l.h:%d l.n:%d\n", l.w, l.h, l.n); // l.w:13 l.h:13 l.n:5
s += l.w*l.h*l.n; // 这里是检测框的个数对应最终feature map的二维点数乘以anchor数目,即13x13x5,网络输出总个数是h*w*anchor_num*(coord_num + conf + class_num),即13*13*5*(5+80)
}
}
fprintf(stderr, "s:%d\n", s); // s:845
return s;
}
- 对于输入图像尺寸为
416 x 416 x 3,经过网络中5个stride = 2的max-pooling尺寸缩小32倍,得到输出的特征图的宽高为13(=416/32)(输出特征图的通道数下面会提到); - 输入图像尺寸
Si x Si,输出特征图宽高为Oi = Si / 2^5; - 最后卷积层输出数目定义的由来:输出图像为Oi x Oi个栅格,每个栅格预测#anchors种boxes大小,每个box包含4个坐标值(x,y,h,w,即中心点坐标+宽度和高度偏移量),1个置信度和#classes个条件类别概率,所以输出维度是
Oi x Oi x #anchors x (5 + #classes); - tiny-yolov2中,输入大小
416 x 416 x 3,输出大小13 x 13 x 425,其中的输出通道个数425,也即最后卷积层的输出通道个数的计算就是根据:输出宽度 x 输出高度 x anchors数目 x (坐标信息数目 + 类别数目)得到的,除去图像二维的乘积,其中要注意坐标信息数目是5(x,y,h,w,conf,conf置信度,其反映是否包含物体以及包含物体情况下位置的准确性,在YOLOv1中的定义为Pr(Object)×IOU^truth_pred,其中Pr(Object)∈{0,1}。),因而是425 = 5 x (4+1+80)。
3.1.2 检测层:fill_network_boxes
detection *dets = make_network_boxes(net, thresh, num);对检测框的结构体数组变量初始化结束后,紧接着是填充初始化的结构体,即fill_network_boxes(net, w, h, thresh, hier, map, relative, dets);,该函数实现位于src/network.c:569:
void fill_network_boxes(network *net, int w, int h, float thresh, float hier, int *map, int relative, detection *dets)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== fill_network_boxes ====\n");
int j;
for(j = 0; j < net->n; ++j){
layer l = net->layers[j];
if(l.type == YOLO){
fprintf(stderr, "YOLO\n");
int count = get_yolo_detections(l, w, h, net->w, net->h, thresh, map, relative, dets);
dets += count;
}
if(l.type == REGION){
fprintf(stderr, "REGION\n");
get_region_detections(l, w, h, net->w, net->h, thresh, map, hier, relative, dets);
dets += l.w*l.h*l.n;
}
if(l.type == DETECTION){
fprintf(stderr, "DETECTION\n");
get_detection_detections(l, w, h, thresh, dets);
dets += l.w*l.h*l.n;
}
}
}
与num_detections一样有对YOLO、REGION、DETECTION层类型的if-else分支判断,tiny-yolov2模型走的是l.type == REGION这个分支。
3.1.2.1 检测层:卷积结果到检测信息的解析get_region_detections
那么再看看该分支的get_region_detections这个函数对检测框数组填充过程的实现,换言之,也是对卷积结果向检测框结果的解析过程,该函数位于src/region_layer.c:364,在函数开头和结尾部分,我打印出一些变量的值以方便理解代码:
void get_region_detections(layer l, int w, int h, int netw, int neth, float thresh, int *map, float tree_thresh, int relative, detection *dets)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== get_region_detections ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "l.batch:%d\n", l.batch); // l.batch:1
fprintf(stderr, "dets[%d].mask:%p\n", 0, dets[0].mask); // dets[0].mask:(nil)
//if(!(dets[0].mask))
// fprintf(stderr, "*(dets[%d].mask):%f\n", 0, *(dets[0].mask));
fprintf(stderr, "l.softmax_tree:%p\n", l.softmax_tree); // l.softmax_tree:(nil)
fprintf(stderr, "map:%p\n", map); // map:(nil)
fprintf(stderr, "l.batch:%d\n", l.batch); // l.batch:1
fprintf(stderr, "l.n:%d\n", l.n); // l.n:5
fprintf(stderr, "l.h:%d\n", l.h); // l.h:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.w:%d\n", l.w); // l.w:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.classes:%d\n", l.classes); // l.classes:80
fprintf(stderr, "l.coords:%d\n", l.coords); // l.coords:4
fprintf(stderr, "l.background:%d\n", l.background); // l.background:0
fprintf(stderr, "thresh:%f\n", thresh); // thresh:0.500000, 0.500000 位于example/darknet.c:432-437,if-else在detect部分定义,若用户未定义则该值默认为0.5
fprintf(stderr, "tree_thresh:%f\n", tree_thresh); // tree_thresh:0.500000,位于example/darknet.c同上附近的位置,变量hier,if-else在detect部分定义为0.5
int i,j,n,z;
float *predictions = l.output;
if (l.batch == 2) {
float *flip = l.output + l.outputs;
for (j = 0; j < l.h; ++j) {
for (i = 0; i < l.w/2; ++i) {
for (n = 0; n < l.n; ++n) {
for(z = 0; z < l.classes + l.coords + 1; ++z){
int i1 = z*l.w*l.h*l.n + n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + i;
int i2 = z*l.w*l.h*l.n + n*l.w*l.h + j*l.w + (l.w - i - 1);
float swap = flip[i1];
flip[i1] = flip[i2];
flip[i2] = swap;
if(z == 0){
flip[i1] = -flip[i1];
flip[i2] = -flip[i2];
}
}
}
}
}
for(i = 0; i < l.outputs; ++i){
l.output[i] = (l.output[i] + flip[i])/2.;
}
}
for (i = 0; i < l.w*l.h; ++i){
int row = i / l.w;
int col = i % l.w;
for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){
int index = n*l.w*l.h + i;
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j){
dets[index].prob[j] = 0;
}
int obj_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords);
int box_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, 0);
int mask_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, 4);
float scale = l.background ? 1 : predictions[obj_index];
dets[index].bbox = get_region_box(predictions, l.biases, n, box_index, col, row, l.w, l.h, l.w*l.h);
dets[index].objectness = scale > thresh ? scale : 0;
if(dets[index].mask){
for(j = 0; j < l.coords - 4; ++j){
dets[index].mask[j] = l.output[mask_index + j*l.w*l.h];
}
}
int class_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords + !l.background);
if(l.softmax_tree){
hierarchy_predictions(predictions + class_index, l.classes, l.softmax_tree, 0, l.w*l.h);
if(map){
for(j = 0; j < 200; ++j){
int class_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords + 1 + map[j]);
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index];
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : 0;
}
} else {
int j = hierarchy_top_prediction(predictions + class_index, l.softmax_tree, tree_thresh, l.w*l.h);
dets[index].prob[j] = (scale > thresh) ? scale : 0;
}
} else {
if(dets[index].objectness){
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j){
int class_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords + 1 + j);
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index];
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : 0;
}
}
}
}
}
fprintf(stderr, "l.w:%d\n", l.w); // l.w:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.h:%d\n", l.h); // l.h:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.n:%d\n", l.n); // l.n:5
fprintf(stderr, "w:%d\n", w); // w:768
fprintf(stderr, "h:%d\n", h); // h:576
fprintf(stderr, "netw:%d\n", netw); // netw:416
fprintf(stderr, "neth:%d\n", neth); // neth:416
fprintf(stderr, "relative:%d\n", relative); // relative:1
correct_region_boxes(dets, l.w*l.h*l.n, w, h, netw, neth, relative);
}
这个函数非常冗长,我在该函数内加入打印信息,可以看到有些指针是空的,这样将代码中if-else不会走到的地方、没有用到的变量都移除掉,可进一步简化get_region_detections为如下流程和代码:
- 初始化检测框中的所有类别概率;
- 根据box索引求解region box检测框,并根据obj索引计算概率判断检测框有效性;
- 对有效的检测框,根据class索引判断有效的物体得到类别概率;
- 对检测框的长度依据原始图像修正,得到x,y,w,h的new_h/neth, new_w/netw的比值。
void get_region_detections(layer l, int w, int h, int netw, int neth, float thresh, int *map, float tree_thresh, int relative, detection *dets)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== get_region_detections ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "l.batch:%d\n", l.batch); // l.batch:1
fprintf(stderr, "dets[%d].mask:%p\n", 0, dets[0].mask); // dets[0].mask:(nil)
//if(!(dets[0].mask))
// fprintf(stderr, "*(dets[%d].mask):%f\n", 0, *(dets[0].mask));
fprintf(stderr, "l.softmax_tree:%p\n", l.softmax_tree); // l.softmax_tree:(nil)
fprintf(stderr, "map:%p\n", map); // map:(nil)
fprintf(stderr, "l.batch:%d\n", l.batch); // l.batch:1
fprintf(stderr, "l.n:%d\n", l.n); // l.n:5
fprintf(stderr, "l.h:%d\n", l.h); // l.h:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.w:%d\n", l.w); // l.w:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.classes:%d\n", l.classes); // l.classes:80
fprintf(stderr, "l.coords:%d\n", l.coords); // l.coords:4
fprintf(stderr, "l.background:%d\n", l.background); // l.background:0
fprintf(stderr, "thresh:%f\n", thresh); // thresh:0.500000, 0.500000 位于example/darknet.c:432-437,if-else在detect部分定义,若用户未定义则该值默认为0.5。后面两次用到(1. 物体存在与否的阈值,2. 类别存在与否的阈值)
fprintf(stderr, "tree_thresh:%f\n", tree_thresh); // tree_thresh:0.500000,位于example/darknet.c同上附近的位置,变量hier,if-else在detect部分定义为0.5
fprintf(stderr, "l.nbiases:%d\n", l.nbiases); // l.nbiases:0,注意这个biases成员是卷积的,而不是anchor的
for(int i=0; i<2*n; i++) {
fprintf(stderr, "l.biases[%d]:%f\n", i, l.biases[i]); // 注:这个是anchor的biases,即anchor的值(和卷积的biases无关),其数值与cfg文件的anchors值一致。一般该数组元素个数是2*n,n是anchor个数。anchor是否与原图匹配的定义是cfg文件中的bias_match,bias_match用在region_layer.c 的 forward_region_layer 中推算预测的检测框的w和h前的判断。
}
int i,j,n;
float *predictions = l.output;
for (i = 0; i < l.w*l.h; ++i){
int row = i / l.w; // 行优先存储,计算当前行数与列数
int col = i % l.w;
/* 1. 初始化检测框中的所有类别概率 */
for(n = 0; n < l.n; ++n){
int index = n*l.w*l.h + i; // 计算结果feature map的下标index[0,n*l.w*l.h),也即检测框数组dets中的第index个检测框元素
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j){ // 初始化n*l.w*l.h个检测框的l.classes个类别对应的概率值
dets[index].prob[j] = 0; // 初始化第 index 个检测框对应类别 j 的概率
}
/* 2. 根据box索引求解region box检测框,并根据obj索引计算概率判断检测框有效性 */
// 拿到第 index 个检测框对应结果feature map的obj下标与box下标
int obj_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords); // index == n*l.w*l.h + i,obj包含1个信息: conf
int box_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, 0); // index == n*l.w*l.h + i,box包含4个信息:x,y,h,w
// 获取第 index 个检测框的类别 prob 缩放系数
float scale = l.background ? 1 : predictions[obj_index]; // l.background:0
dets[index].bbox = get_region_box(predictions, l.biases, n, box_index, col, row, l.w, l.h, l.w*l.h);
dets[index].objectness = scale > thresh ? scale : 0; // 判断第 index 个框内是否有物体,根据是否大于预设的默认的0.5,决定第 index 个检测框的结果featuremap的值是否有意义(若有意义则取出如下的prob信息)
/* 3. 对有效的检测框,根据class索引判断有效的物体得到类别概率 */
// 若第 index 个检测框有意义,则取出所有类的概率
// 逐一取出对应类别概率在输出的feature map的值并判断与阈值的大小关系
if(dets[index].objectness){
for(j = 0; j < l.classes; ++j){
int class_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords + 1 + j);
float prob = scale*predictions[class_index];
dets[index].prob[j] = (prob > thresh) ? prob : 0;
}
}
}
}
fprintf(stderr, "l.w:%d\n", l.w); // l.w:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.h:%d\n", l.h); // l.h:13
fprintf(stderr, "l.n:%d\n", l.n); // l.n:5
fprintf(stderr, "w:%d\n", w); // w:768
fprintf(stderr, "h:%d\n", h); // h:576
fprintf(stderr, "netw:%d\n", netw); // netw:416
fprintf(stderr, "neth:%d\n", neth); // neth:416
fprintf(stderr, "relative:%d\n", relative); // relative:1
/* 4. 对检测框的长度依据原始图像修正,得到x,y,w,h的new_h/neth, new_w/netw的比值 */
correct_region_boxes(dets, l.w*l.h*l.n, w, h, netw, neth, relative);
}
int entry_index(layer l, int batch, int location, int entry)
{
// obj_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords); // l.coords: 4, i: [0, l.w*l.h)
// box_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, 0); // i: [0, l.w*l.h)
// class_index = entry_index(l, 0, n*l.w*l.h + i, l.coords + 1 + j); // j: [0, l.classes)
int n = location / (l.w*l.h); // 第 n 个anchor, n: [0, max_anchors_num),
int loc = location % (l.w*l.h); // 第 n 个 anchor 中的第 loc 个框, loc: [0, l.w*l.h)
// 第batch个(本例为0),batch=1时总的输出feature map元素数目:5*13*13*(80+4+1),
// 第 n 个anchor,因而是 n * l.w * l.h * (l.coords+l.classes+1),多+1是conf置信度(其反映是否包含物体以及包含物体情况下位置的准确性,具体见上文)
return batch*l.outputs + n*l.w*l.h*(l.coords+l.classes+1) + entry*l.w*l.h + loc;
}
box get_region_box(float *x, float *biases, int n, int index, int i, int j, int w, int h, int stride)
{
// get_region_box(predictions, l.biases, n, box_index, col, row, l.w, l.h, l.w*l.h);
// row: [0, l.h), col: [0, l.w)
box b;
b.x = (i + x[index + 0*stride]) / w;
b.y = (j + x[index + 1*stride]) / h;
b.w = exp(x[index + 2*stride]) * biases[2*n] / w; // 这里biases是anchors的值,biases[2*n]和[2*n+1]分别对应w与h的放缩比例
b.h = exp(x[index + 3*stride]) * biases[2*n+1] / h;
return b;
}
下面是第4部分correct_region_boxes:修正region boxes,对检测框的长度依据原始图像修正,得到x,y,w,h的new_h/neth, new_w/netw的比值,用于后续draw_detections的调用。
void correct_region_boxes(detection *dets, int n, int w, int h, int netw, int neth, int relative)
{
fprintf(stderr, "==== correct_region_boxes ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "n:%d\n", n); // n:845
fprintf(stderr, "w:%d\n", w); // w:768
fprintf(stderr, "h:%d\n", h); // h:576
fprintf(stderr, "netw:%d\n", netw); // netw:416
fprintf(stderr, "neth:%d\n", neth); // neth:416
fprintf(stderr, "relative:%d\n", relative); // relative:1
/* 根据网络输入大小,重新调整检测框的位置信息。
将原图等比例缩放,确保缩放后的图不会超出网络输入大小
(等比例缩放过程中将宽高中的较大值,
网络输入对应的宽或高,进行等比例缩放)。
*/
int i;
int new_w=0;
int new_h=0;
if (((float)netw/w) < ((float)neth/h)) {
new_w = netw;
new_h = (h * netw)/w;
} else {
new_h = neth;
new_w = (w * neth)/h;
}
fprintf(stderr, "new_h:%d\n", new_h); // new_h:312
fprintf(stderr, "new_w:%d\n", new_w); // new_w:416
/* 遍历所有检测框,根据比例调整x,y,h,w */
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i){
box b = dets[i].bbox;
fprintf(stderr, "1 b.x:%f b.y:%f b.h:%f b.w:%f\n", b.x, b.y, b.h, b.w);
// 1 b.x:0.034133 b.y:0.038086 b.h:0.018859 b.w:0.022933
// b.x/和b.y原本的计算,是先对原图resize等比例到网络输入大小,计算所在比例值
// b.h, b.w应该同上
// x,y,w,h都乘以新的比率更新,再乘以该比例系数: (netw/new_w) 或 (neth/new_h)
// x, y的除,等同于乘系数
b.x = (b.x - (netw - new_w)/2./netw) / ((float)new_w/netw); // 先减new_w带来的偏移量的原有占比,再除系数的倒数(=乘系数)
b.y = (b.y - (neth - new_h)/2./neth) / ((float)new_h/neth);
b.w *= (float)netw/new_w;
b.h *= (float)neth/new_h;
if(!relative){ // relative:1
b.x *= w;
b.w *= w;
b.y *= h;
b.h *= h;
}
fprintf(stderr, "2 b.x:%f b.y:%f b.h:%f b.w:%f\n", b.x, b.y, b.h, b.w);
// 2 b.x:0.034133 b.y:-0.115885 b.h:0.025146 b.w:0.022933
dets[i].bbox = b;
}
}
为了更清楚阐明几个检测信息,查了draw_detections时调用box里的x,y,w,h处的代码,计算得到检测框的上下左右四个值:
im.w和im.h分别为原图的列数与行数;x、y: 分别对应检测框中心点的横、纵坐标(的比例值);h、w:分别对应检测框高度和宽度(的比例值)。
int left = (b.x-b.w/2.)*im.w;
int right = (b.x+b.w/2.)*im.w;
int top = (b.y-b.h/2.)*im.h;
int bot = (b.y+b.h/2.)*im.h;
以上,便分析完了网络检测部分的get_network_boxes。
3.1.3 检测层:region过程总结
简单总结下region前向过程,这部分不仅申请检测框的空间和初始化工作,同时也根据网络最后一个卷积的输出feature map做了相应的计算,转化为对应检测框结构体中的中心点、检测框长宽信息、每个类别概率、每个检测框置信度等信息。并在这个过程中对结果进行了两次筛选:
- 第一次是依据阈值对检测框是否存在物体的if-else筛选;
- 第二次是依据同一个阈值对检测框中物体概率的if-else筛选。
特别需要注意的是,检测框总数目是anchor数乘以feature map的宽高,检测框数目是由最后一个卷积的维度确定的(这包括两个部分:最后卷积的二维大小,即宽高,以及检测框锚点anchor数),其实仔细想想这反而将网络在检测结果的最大框数进行固定了,虽然整个网络是全卷积对输入大小不关心,但在检测这一项,若图像中目标很多,超过预设的13 x 13 x 5,这两个超参数也会对结果造成很大的影响。最后一个卷积的二维维度大小是由stride = 2的卷积或者池化的个数决定的,锚点anchors数目是由用户自己设定的。
我也想了如何自适应设置这两个超参数:
- 卷积,可以跑所有标注图片的数据,看看每张图有多少个框,进而确定总框数设置多少合适,进而设计最后一个卷积层的输出宽高通道数;
- 锚点anchor数目的设定,可以跑出所有标注检测框的比例,当然这部分还需要细致考虑,因为每一种类别的检测框比例有多种,可以依据这个思路更精细地设置锚点。
但在做这些前,需要考量一下这些工作对精度结果的提升预估,从而合理花费时间去设计更值得做的工作。
3.2 检测层:非极大值抑制do_nms_sort
在第一部分将卷积结果转换为检测框信息后,紧接着便是非极大值抑制过程,该过程会对交叠大于某个阈值的两个检测框视为检测到同一个物体,而进行去掉其中一个的操作,该完整操作流程如下:
- 筛选所有可能有物体的检测框。即通过交换,让检测框数组中前
total个的检测框均符合dets[i].objectness!=0; - 逐类去掉重复检测框。在锁定某个类别 k 后
sort_class = k:- 对
total个检测框,依据第 k 类进行降序排序; - 两层循环计算检测框
dets[i]与检测框dets[j]的IOU(intersection of union):- 若
box_iou(dets[i], dets[j]) > thresh,则在第 k 类的检测结果中去掉检测框dets[j](即前面按照第 k 类降序排列,k类概率小的框),将该检测框对应第 k 类概率置为 0 ,即dets[j].prob[k] = 0,后面再在第 k 类中遇到该框时直接continue跳过; - 若
box_iou(dets[i], dets[j]) <= thresh,则说明没有两个检测框重叠,继续下一个检测框;
- 若
- 重复1,2直至遍历结束完
total个检测框;
- 对
- 重复1,2直至遍历完
classes个类别。
network_predict(net, X);
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", input, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms); // nms:.45,nms值前面写死的0.45,非0会执行do_nms_sort
draw_detections(im, dets, nboxes, thresh, names, alphabet, l.classes);
接下来是第三部分的分析,第三部分是do_nms_sort的计算,先找到并给出该函数的位置和代码./src/box.c:58:
void do_nms_sort(detection *dets, int total, int classes, float thresh)
{
// do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms); // nms: .45
fprintf(stderr, "==== do_nms_sort ====\n");
fprintf(stderr, "total:%d\n", total); // total:845, nboxes
fprintf(stderr, "classes:%d\n", classes); // classes:80
fprintf(stderr, "thresh:%f\n", thresh); // thresh:0.450000
// 遍历所有total个检测框,之后,得到有意义的 (k+1) 个检测框
// 将有意义的检测框(即dets[i].objectness非0的)放到检测框数组的前面,
// 交换后面的检测框(不确保是否objectness的值)与无意义的检测框,
// 因为--i的缘故,不确保是否有意义的检测框紧接着又会进行判断,从而决定是否交换,
// 直到k的值被自减到最后一个有意义的检测框,也即for循环结束(因k从0计,因而总的有意义检测框是(k+1))。
int i, j, k;
k = total-1;
for(i = 0; i <= k; ++i){
if(dets[i].objectness == 0){
detection swap = dets[i];
dets[i] = dets[k];
dets[k] = swap;
--k;
--i;
}
}
total = k+1;
// 逐类别,对所有检测框去重
// 遍历 classes 个类别,
// 先选中该类别,即设定sort_class的值,再对所有有意义的检测框按照类别 k 的概率降序排序
// 比较两个检测框 i, j 的重叠是否大于阈值,大于该阈值说明可能是同一个物体,去掉概率低的(框j),同时设置框 j 第 k 类的概率为 0(后面遇到则continue跳过),即执行了检测框的去重操作
for(k = 0; k < classes; ++k){
for(i = 0; i < total; ++i){
dets[i].sort_class = k;
}
qsort(dets, total, sizeof(detection), nms_comparator);
for(i = 0; i < total; ++i){
if(dets[i].prob[k] == 0) continue;
box a = dets[i].bbox;
for(j = i+1; j < total; ++j){
box b = dets[j].bbox;
if (box_iou(a, b) > thresh){
dets[j].prob[k] = 0;
}
}
}
}
}
// qsort的比较函数,用来比较第 k 类时候概率大小
int nms_comparator(const void *pa, const void *pb)
{
detection a = *(detection *)pa;
detection b = *(detection *)pb;
float diff = 0;
if(b.sort_class >= 0){ // 多类时,sort_class在do_nms_sort中定义就是在这里按照第sort_class类进行排序
diff = a.prob[b.sort_class] - b.prob[b.sort_class];
} else { // 这里,我猜想是只有1类的情形
diff = a.objectness - b.objectness;
}
if(diff < 0) return 1;
else if(diff > 0) return -1;
return 0;
}
// iou,intersection of union,
// 即交集占并集的比例
float box_iou(box a, box b)
{
return box_intersection(a, b)/box_union(a, b);
}
// 由overlap得到横纵方向上的重叠长度,
// 若两个重叠长度其一小于0则说明两个框没有交叠的地方,即没有交集直接返回0,
// 否则有重叠,重叠面积为两个方向重叠长度的乘积
float box_intersection(box a, box b)
{
float w = overlap(a.x, a.w, b.x, b.w);
float h = overlap(a.y, a.h, b.y, b.h);
if(w < 0 || h < 0) return 0;
float area = w*h;
return area;
}
// 由a,b检测框各自的面积减去二者交集的面积,
// 即为并集的面积
float box_union(box a, box b)
{
float i = box_intersection(a, b);
float u = a.w*a.h + b.w*b.h - i;
return u;
}
// 看懂这个函数需要画两个重叠的框,
// 设置中心点的横纵坐标分别为(x1,y1)、(x2,y2),
// 就会清楚最后得到的结果是一个方向上重叠的长度
float overlap(float x1, float w1, float x2, float w2)
{
float l1 = x1 - w1/2;
float l2 = x2 - w2/2;
float left = l1 > l2 ? l1 : l2;
float r1 = x1 + w1/2;
float r2 = x2 + w2/2;
float right = r1 < r2 ? r1 : r2;
return right - left;
}
以上便是 Darknet 对于检测层的前向计算,更具体的见下方的流程图:

